Using Statistical Volatility Indicators for Smarter Trading
Understanding when markets are most active is a game-changer for traders. High-volatility periods, or “Killzones,” provide unique opportunities to capture significant price movements. Stat-Map’s Statistical Volatility Indicator equips traders with the tools to pinpoint these critical times, improving timing precision and risk management.
What Is the Statistical Volatility Indicator?
Stat-Map’s Statistical Volatility Indicator is a dynamic tool designed to help traders identify “Killzones”—periods of peak market activity. These windows often correspond to overlaps in global trading sessions, market openings or closings, and major economic announcements. By visually mapping out volatility trends over time, the indicator empowers traders to make data-driven decisions about when to trade, ensuring they focus their efforts during the most promising hours.
The tool uses two visualization methods:
• Heatmap: A color-coded display showing high- and low-volatility times at a glance.
• Bar Chart: A detailed breakdown of volatility trends, with a midline separating high- and low-volatility ranges.
This combination makes the Statistical Volatility Indicator an essential tool for traders looking to optimize their strategies and minimize exposure to unproductive market conditions.
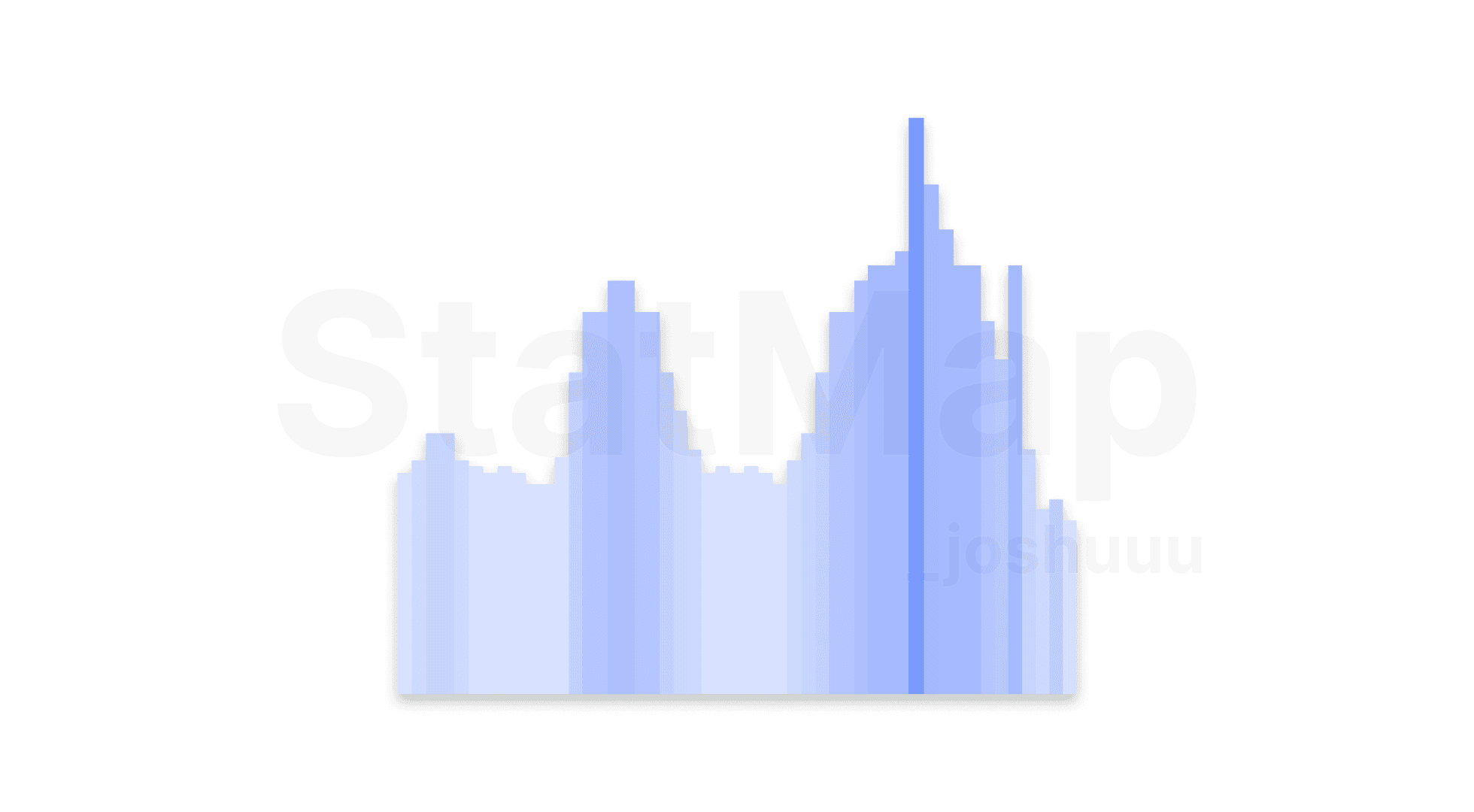
Understanding the Volatility Graph
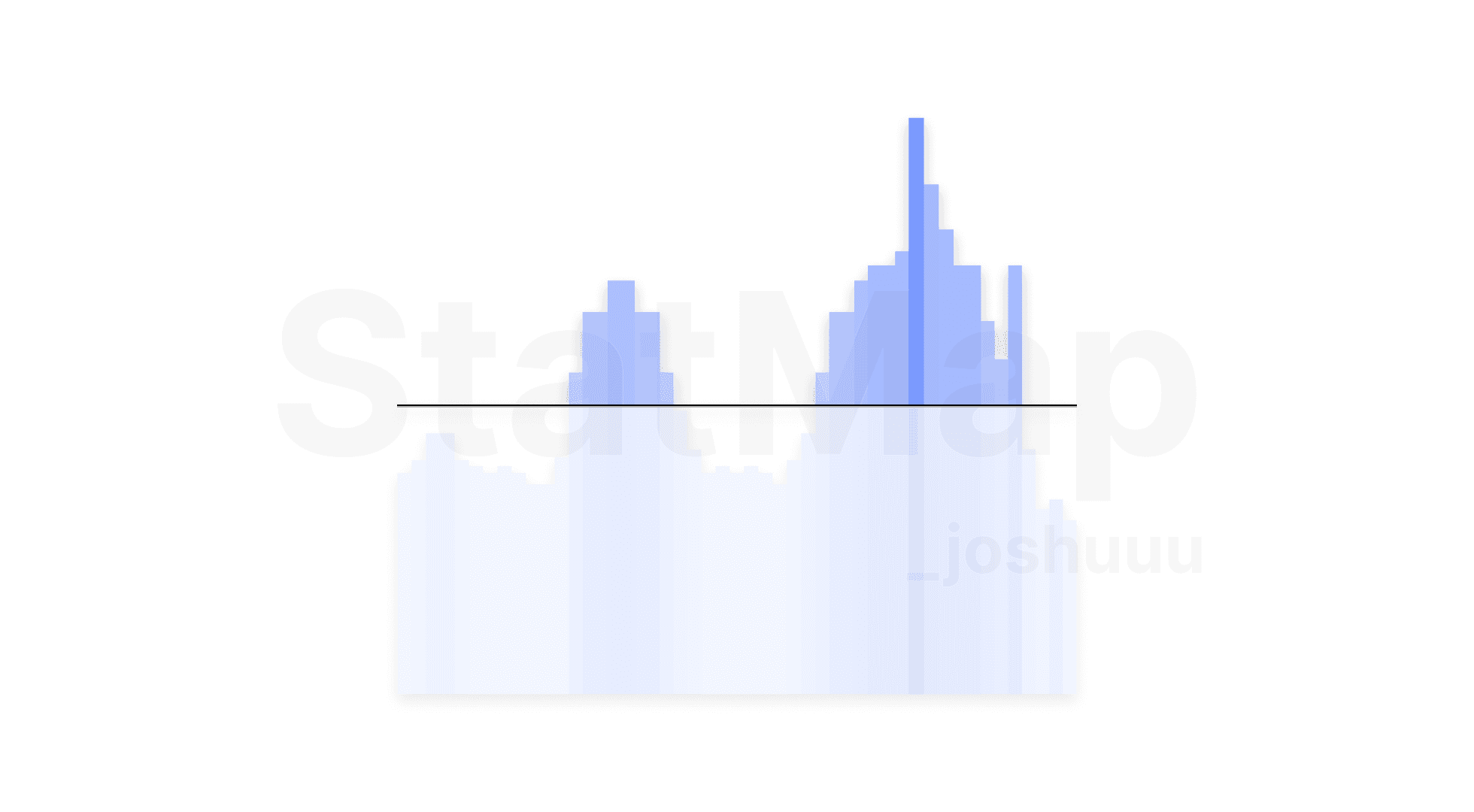
The bar chart provided by the Statistical Volatility Indicator features a midline representing the 50% level of the max-to-min volatility range. The graph is divided into two zones:
Above the Midline (High Volatility):
This region signals periods of increased price movement, driven by institutional activity, news events, or overlapping trading sessions. Traders can expect larger price swings, creating opportunities for trend trading or scalping strategies.
Below the Midline (Low Volatility):
Times below the midline indicate quieter periods, often marked by reduced trading activity and smaller price ranges. These periods are more prone to stagnation or choppy, directionless movement, which can lead to unproductive trades.
By clearly distinguishing between these zones, traders gain a clearer understanding of when the market is likely to provide actionable opportunities.

Why Focus on High Volatility?
When using the Statistical Volatility Indicator, traders often blur out or ignore the lower half of the graph below the midline. Why? Because periods of greater volatility offer:
Expansion Opportunities:
High-volatility times are typically when the market moves out of consolidation phases and into trending or breakout patterns. This is where most trading profits are made.
Improved Risk-to-Reward Ratios:
Larger price swings allow traders to set wider targets while maintaining manageable stop losses.
Reduced Market Noise:
Low-volatility periods often see price movement dominated by random fluctuations, making it harder to identify trends or execute effective strategies.
By focusing on the upper 50% of the chart, traders can concentrate their efforts on periods most likely to result in meaningful price action.
Stat-Map’s Statistical Volatility Indicator is a powerful tool for identifying Killzones and optimizing trading strategies. By focusing on periods of high volatility, traders can capture significant price movements, improve risk-to-reward ratios, and reduce exposure to low-productivity market noise. Whether you’re a day trader or a long-term strategist, integrating this tool into your approach can refine your timing and maximize your trading potential.
Related Articles
Combining StatMap and StatVol
Learn three powerful ways to combine StatMap and StatVol indicators for high-probability trading setups using statistical displacements and key levels...
Custom Daily Anchor
Learn how to customize the daily anchor for your trading indicators to better align with your instrument's active session.